Concentric cylinders can also be considered as co-axial cylinders. The field strength at a radial distance r form an isolated conductor having a charge q coulomb per unit length is given by-
E = q/2πε0ε0r

Fig 1. shows a section of a cable which can be considered as co-axial cylinder. The radius of the inner conductor is a and the radius of the outer sheath is b, the space between the two surfaces being filled with dielectric of permittivity ε. As the surface will coincide with the original equipotential at b, the distribution of field strength over the distance (b – a) will remain unchanged. Hence potential difference the two cylindrical surfaces is V=∫Edr
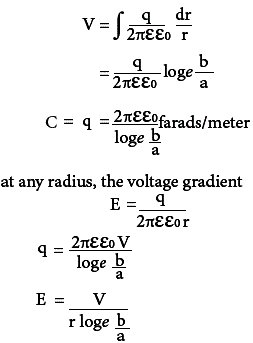
Maximum field strength or voltage gradient is at the surface of the inner conductor whose radius is a and minimum field strength or voltage gradient is at the surface of the outer conductor whose radius is b.

