If number of individual capacitor having a capacitance C1, C2 and C3 are connected in series, then the total capacitance C is found as follows:_
The charge on each capacitor is same so the voltage across each capacitor is V1, V2 and V3 respectively. Show the charge on each capacitor will be:
Q1 = C1V1 ; Q2 = C2V2 ; Q3 = C3V3 ; Q = CV
As the charge on each capacitor is same, Q1 = Q2 = Q3 = Q
Therefore, V1/V = C1/C , V2/V = C2/C , V3/V = C3/C
V = V1 + V2 + V3 in series circuit
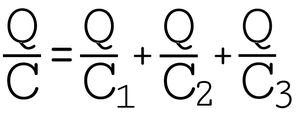
Therefore, it can be found that
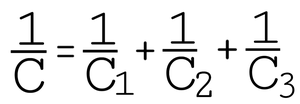
Example 1:- Three capacitors C1, C2 and C3 of the value of 1μ F, 2 μ F and 4 μ F are in series and connected across a potential of 230 V.
a) Calculate total capacitance, b) charge on which capacitor and, c) voltage across which capacitor
The system of capacitors in the example is shown in following figure


= ( 1/1 ) + ( 1/2 ) + ( 1/4 ) = ( 7/4 ) = 1.75
C = ( 4/7 ) = 0.57 μF
Q = CV = 0.57 × 10-6 × 230 = 131 × 10-6 coulomb
Q1 = Q2 = Q3 = Q = 131 × 10-6 coulomb
V1= Q1 /C1 = ( 131 × 10-6 ) / ( 1 × 10-6 )= 131 V
V2= Q2 /C2 = ( 131 × 10-6 ) / ( 2 × 10-6 ) = 65.5 V
V3= Q3 /C3 = ( 131 × 10-6 ) / ( 4 × 10-6 ) = 32.75 V
V1 + V2 + V3 = 131 + 65.5 +32.75 = 229.25 V
Which takes approximately with the total voltage 230 V.
The inverse capacitance ( 1/C ) is called elastance.
So if this term is used, then in case of series capacitors, their total elastance = sum of individual separate elastances.
The above expressions and theory is useful in considering compound dielectrics in electrical Apparatus e.g. dielectric used in the slots of High Voltage machines around the conductor in slot. Another example of composite dielectric is the cable. When the dielectric is homogeneous, the potential gradient is uniform. When the dielectric consists of layer of different materials the different permittivity, the potential gradient is different from each material.
Example 2:- Find the voltage distribution, potential gradient and field strength across the dielectric in capacitor if
A) The dielectric used in homogeneous of thickness 5 mm and a potential difference of 10,000 V is applied across it, the permittivity of the insulating material being 6.
B) If in the same capacitor, two dielectric or insulating materials are used, one of thickness 4 mm and having permittivity 6, while the other of thickness 1 mm and having permittivity 2.
(a) In frst case, E = 10,000/(5 × 10-3) = 2 × 10-6 V / metre.
(b) In second Case, the system Can be considered as capacitance in series Each having capacitance as follows : –
C1 = ε1 ε0 A / d1 = 6 ε0 A / 4 × 10-3 = 1.5 × 10-3 A
C2 = ε2 ε0 A / d2 = 2 ε0 A / 1 × 10-3 = 2 × 10-3 A
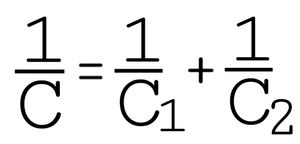
or C = ( C1C2 ) / ( C1+C2 ) = [ ( 1.5 × 103 × 2 × 103 ) / ( 1.5 × 103 + 2 × 103 ) ] ε0 A
=[ ( 3 × 106 ) / ( 3.5 × 103 ) ] ε0 A
=0.857 × 103 ε0 A
Voltage across first dielectri V1 = C / C1 × V
= [(0.857 × 103) / ( 2 × 103 )] × 103 V
E1 = V1 / 4 × 10-3 = 5715 / 4 = 1429 × 106 V/m
E2 = V2 / 1 × 10-3 = 4285 / 4 = 0.429 × 106 V/m
